If you’re looking for a seafood source that blends tradition, technology, and environmental responsibility, Iran’s shrimp farming process delivers exactly that. With its warm coastal waters and expanding aquaculture infrastructure, Iran has become a rising player in the global shrimp market. The shrimp farming process here is not only efficient but also aligned with international standards, making Iranian shrimp a reliable choice for importers and distributors worldwide.
From hatchery to harvest, Iranian farms follow a structured approach that includes SPF broodstock, biosecure grow-out ponds, and advanced water quality monitoring. These steps ensure high survival rates, minimal antibiotic use, and consistent product quality. The process is backed by national fisheries programs and supported by scientific research from Iranian universities and international bodies like FAO.
Whether you’re a seafood buyer, wholesaler, or simply curious about sustainable aquaculture, understanding the shrimp farming process in Iran offers valuable insights into a fast-growing industry. Keep reading to explore how Iran is redefining shrimp production with precision and purpose.
Strategic Location: Why Iran’s Coastal Geography Favors Shrimp Farming
Iran’s southern coastline, stretching over 1,800 kilometers along the Persian Gulf and Sea of Oman, offers a unique ecological advantage for shrimp aquaculture. The warm, saline waters are rich in plankton and minerals, creating ideal conditions for the shrimp farming process. Provinces like Hormozgan, Bushehr, and Sistan-Baluchestan have become key hubs for shrimp production due to their stable climate and access to clean seawater.
Key geographic advantages:
- Stable water temperature: Promotes year-round farming cycles
- Low pollution levels: Reduces disease outbreaks
- Natural salinity: Enhances shrimp flavor and texture
One of the leading producers in this region is Pishva Holding, which has strategically located its farms to maximize these environmental benefits. Their shrimp farming process begins with water filtration and quality testing, ensuring optimal conditions before stocking post-larvae.
Iran’s coastal geography also supports logistics, with proximity to major ports like Bandar Abbas and Bushehr facilitating exports to Asia, Europe, and the Gulf. This geographic positioning reduces transit time and preserves product freshness.
For buyers seeking consistency and quality, Iran’s coastal setup offers a natural edge. The shrimp farming process here isn’t just about production—it’s about leveraging nature to deliver premium seafood.
Hatchery Phase: Controlled Breeding and Larval Development
The hatchery phase is the foundation of a successful shrimp farming process. In Iran, hatcheries use SPF (Specific Pathogen-Free) broodstock sourced from certified suppliers to ensure disease resistance and genetic quality. This phase includes maturation, spawning, larval rearing, and post-larvae (PL) development.
Steps in the hatchery phase:
- Broodstock conditioning: Controlled lighting and temperature
- Spawning tanks: Monitored for water quality and oxygen levels
- Larval rearing: Fed with microalgae and Artemia
- PL grading: Ensures uniform size and health
As an Iranian Shrimp Supplier & Wholesale provider, companies like Shrimpy Co. and Pishva Holding invest heavily in hatchery infrastructure. Their facilities follow FAO and Iranian Fisheries Organization guidelines, using recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) to minimize water usage and improve biosecurity.
Iran’s hatchery success is reflected in its high PL survival rates, often exceeding 70%, which is competitive with global standards. This efficiency reduces costs and improves farm productivity downstream.
For importers and distributors, sourcing from an Iranian Shrimp Supplier & Wholesale partner means access to shrimp that’s strong from the start—bred with precision and care.
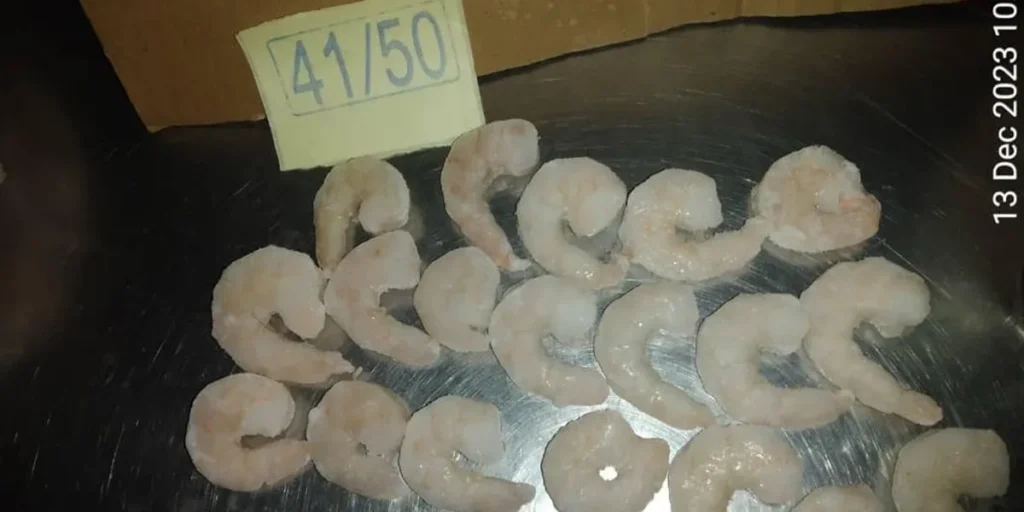

Grow-Out Farms: Semi-Intensive and Intensive Systems
The grow-out stage is where shrimp transition from post-larvae to market size. Iran’s shrimp farming process typically uses semi-intensive systems, but newer farms are adopting intensive methods to boost yield and efficiency. These systems include aeration, automatic feeders, and smart monitoring tools.
Comparison of farming systems:
| System Type | Stocking Density | Technology Used | Output Quality |
| Semi-Intensive | 20–30 PL/m² | Manual feeding, basic aeration | Moderate, cost-effective |
| Intensive | 60–100 PL/m² | Smart sensors, auto feeders | High quality and cost effective shrimp |
Iranian farms are increasingly using probiotic feeds and water recycling to reduce antibiotic use and environmental impact. According to the Journal of Fisheries Research, aeration and water quality control significantly improve shrimp growth rates and reduce mortality.
This evolution in the shrimp farming process allows Iranian producers to offer high quality and cost effective shrimp to global markets. Buyers benefit from consistent sizing, better texture, and lower rejection rates at customs.
For wholesalers and retailers, Iran’s grow-out farms represent a smart sourcing option—combining technology with affordability.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling: Preserving Quality
Harvesting is a critical step in the shrimp farming process, where months of effort culminate in product collection. Iranian farms typically harvest shrimp manually or with mechanical nets, depending on scale. Immediate transfer to ice slurry tanks helps preserve freshness and reduce metabolic stress.
Post-harvest steps:
- Grading: Shrimp sorted by size and quality
- Washing: Removal of debris and impurities
- De-heading and peeling: For value-added formats
- Freezing: IQF or block freezing for export
Iranian processors follow HACCP and ISO 22000 standards, ensuring compliance with EU and GCC regulations. Facilities like those operated by Pishva Holding use blast freezers and traceability systems to maintain product integrity.
According to a 2023 review in Food and Bioprocess Technology, proper post-harvest handling can extend shrimp shelf life by up to 40% and preserve nutritional value. Iranian producers are aligning with these best practices to meet global expectations.
For buyers, this means shrimp that arrives fresh, safe, and ready for retail or foodservice use.
Export Logistics: From Farm to Global Markets
Export logistics are the final link in the shrimp farming process. Iran’s proximity to major ports like Bandar Abbas and Chabahar enables efficient shipping to Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. Reefer containers and cold chain protocols ensure that shrimp maintains its quality during transit.
Export essentials:
- Documentation: Health certificates, origin reports, antibiotic-free declarations
- Packaging: Bulk frozen, retail packs, vacuum-sealed formats
- Transport modes: Sea freight, air cargo, and land routes
Iranian shrimp exports have grown by over 60% in recent years, with key markets including China, UAE, Russia, and Germany. Companies like Pishva Holding and Varna Trading offer flexible INCOTERMS and multilingual support for importers.
The shrimp farming process in Iran doesn’t end at harvest—it extends to global delivery. With robust infrastructure and government support, Iran is becoming a reliable seafood exporter.
For international buyers, this means fewer delays, better compliance, and consistent product quality.
Conclusion: Why Iran’s Shrimp Farming Process Deserves Global Attention
In today’s seafood industry, efficiency and sustainability are no longer optional—they’re essential. Iran’s shrimp farming process stands out as a model that balances ecological responsibility with commercial viability. By integrating scientific hatchery methods, semi-intensive grow-out systems, and cold-chain logistics, Iranian producers have created a streamlined pipeline from pond to export.
What makes this process particularly compelling is its adaptability. Farms are increasingly adopting smart technologies like automated feeders, aeration systems, and real-time water sensors. These innovations not only improve shrimp health but also reduce environmental impact—a win-win for producers and consumers alike.
Iran’s strategic location along the Persian Gulf further enhances its export potential, offering easy access to markets in Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. With government support and international certifications in place, the shrimp farming process in Iran is poised for continued growth.
For stakeholders across the seafood value chain, Iran offers more than just shrimp—it offers a smarter way to farm. If you’re seeking quality, consistency, and sustainability, this is a farming model worth watching.
FAQ
1: What makes Iran ideal for shrimp farming?
Its warm, saline coastal waters and stable climate create optimal conditions for shrimp growth.
2: Are Iranian hatcheries certified?
Yes, most use SPF broodstock and follow FAO and national guidelines.
3: What farming systems are used in Iran?
Both semi-intensive and intensive systems, with increasing use of smart technologies.
4: How is shrimp quality preserved after harvest?
Through ice slurry tanks, IQF freezing, and HACCP-compliant processing.
5: Can Iranian shrimp be exported globally?
Absolutely. Iran exports to China, UAE, Russia, and Europe with full documentation and cold chain logistics.