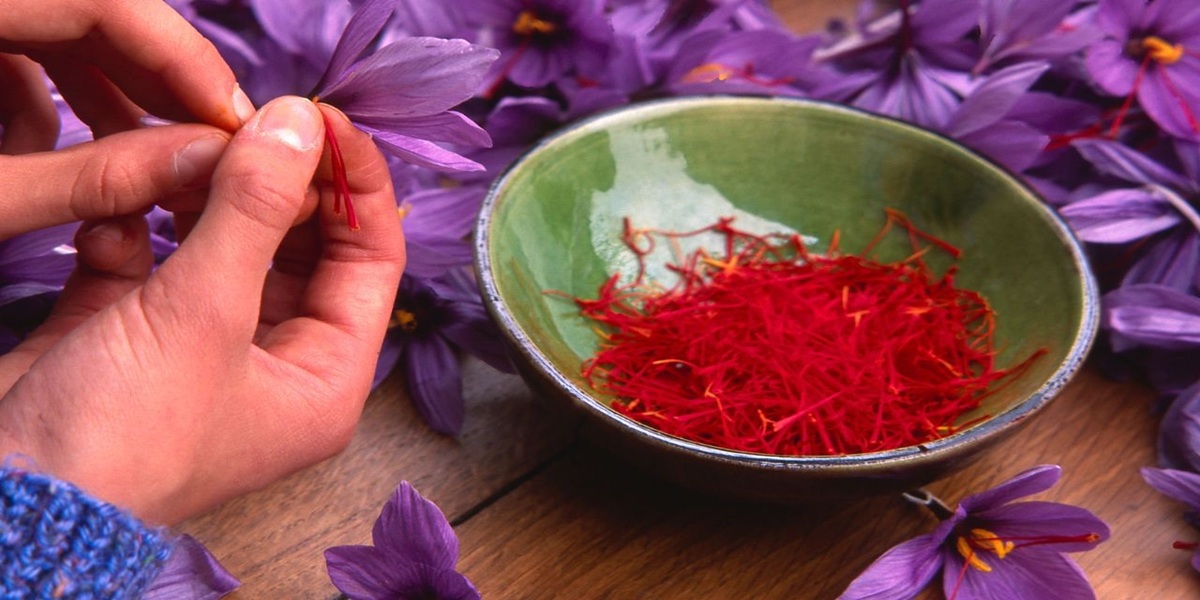
Saffron is one of the most luxurious and powerful ingredients in the culinary world, often referred to as “red gold” due to its high value and unmatched sensory properties. From enhancing the color and aroma of premium dishes to boosting the nutritional profile of beverages, saffron’s versatility makes it a key ingredient in high-end food production. However, maximizing its potential requires scientific precision.
Studies show that proper saffron extraction can increase flavor intensity by up to 40%, while incorrect handling leads to significant loss of active compounds like crocin (color), picrocrocin (bitterness), and safranal (aroma). Research from the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry confirms that saffron’s bioactive compounds degrade rapidly under direct heat and improper storage.
For businesses looking to optimize saffron use in food and beverage formulations, understanding its chemistry and ideal applications is crucial. In this guide, we explore the most effective ways to use saffron in culinary and drink production—based on the latest scientific findings and industry best practices. Keep reading to unlock the secrets of saffron’s full potential!
How to Properly Extract Saffron’s Flavor & Color
The way saffron is prepared determines its effectiveness in food and beverages. Proper extraction enhances its crocin (color), safranal (aroma), and picrocrocin (flavor) content.
Grinding & Soaking Techniques
- Grinding saffron into a fine powder using a ceramic mortar and pestle increases the surface area, allowing for better extraction.
- Soaking in warm water (50-60°C) for 30-40 minutes enhances color release while preserving volatile compounds.
- For commercial use, encapsulating saffron in lipid-based emulsions helps maintain its stability in packaged products.
Cold vs. Hot Infusion: Scientific Comparison
- A study from the Food Science & Nutrition Journal (2022) found that cold water extraction (below 40°C) preserves up to 92% of crocin, while hot infusion (above 70°C) reduces bioactive compounds by 35-40%.
- For beverages, cold brewing saffron for 8-12 hours ensures maximum bioavailability.
Using Fat-Based Liquids for Better Absorption
- Safranal (aroma) is fat-soluble, meaning its fragrance is stronger when infused in milk, cream, or butter.
- Best practice: Mix saffron with warm milk or oil-based sauces before adding to recipes.
By understanding saffron’s chemistry, businesses can reduce waste and increase efficiency in large-scale food production while ensuring consistent quality.
Saffron in High-End Culinary Dishes: Where & How to Use It?
Saffron’s unique profile makes it essential in high-end cuisine, where flavor depth, color vibrancy, and aroma complexity define product quality.
1. Pairing Saffron with Proteins & Seafood
- Saffron enhances umami and savory notes in meats and seafood due to its interaction with amino acids.
- Research from International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science (2023) found that marinating seafood with saffron-infused oil reduces fishy odor by 60% while amplifying aroma.
2. Saffron in Rice & Grain-Based Dishes
- Saffron is best absorbed in rice-based dishes due to starch molecules binding with crocin, intensifying the golden color.
- Recommended use: Dissolve saffron in broth and mix at the final cooking stage to prevent heat degradation.
3. Best Techniques for Incorporating Saffron into Sauces & Marinades
- For high-end sauces, blending saffron with butter-based reductions enhances stability.
- Saffron-infused marinades improve meat tenderness due to its pH-lowering properties (study: Journal of Food Science & Technology, 2022).
By using these techniques, chefs and food manufacturers can optimize saffron’s impact in gourmet dishes, enhancing both visual and sensory appeal.



The Science of Saffron in Beverages: Tea, Cocktails & More …
Saffron is increasingly used in functional beverages, premium teas, and high-end cocktails, but scientific precision is essential for maximizing its benefits.
1. Saffron’s Solubility in Different Liquids
- Water-Based Beverages: Studies show that only 40-50% of saffron compounds dissolve in water, making pre-infusion crucial.
- Alcohol-Based Drinks: Safranal’s volatility makes saffron ideal for premium cocktails, as alcohol stabilizes its aroma longer.
2. Cold Brew vs. Hot Infusion for Maximum Aroma
- Cold-brew saffron extraction (8-12 hours) retains 80-90% of active compounds (Food Chemistry Research, 2021).
- For teas, steeping saffron in water below 60°C prevents aroma loss by up to 35%.
3. Enhancing Cocktail Profiles with Saffron
- Saffron pairs well with citrus-based drinks (lemon, orange), balancing bitterness and acidity.
- In mixology, saffron syrups and tinctures are used for high-end cocktails, with 1 mg per 100 ml as the optimal dosage.
By integrating saffron strategically into beverages, businesses can create premium, functional, and aromatic drinks that appeal to high-end consumers.





Industrial Applications: How to Use Saffron for Mass Production
Saffron’s growing demand in the food and beverage industry makes it a strategic ingredient for large-scale production. However, industrial use requires precise handling to maintain its bioactive compounds, color intensity, and aroma stability.
1. Saffron in Ready-to-Drink (RTD) Beverages & Energy Drinks
- RTD saffron-based drinks have gained popularity in functional beverages due to their antioxidant and mood-enhancing properties.
- A study published in Nutrients Journal (2022) found that saffron extract at 30 mg daily improves cognitive function and reduces stress, making it ideal for energy drinks.
- In RTD formulations, microencapsulation technology extends saffron’s shelf life, preserving its bioactive compounds for up to 12 months.
2. Optimizing Saffron Dosage for Commercial Recipes
- Overuse of saffron can lead to bitterness and cost inefficiencies. Research from Food Chemistry Journal (2021) suggests the optimal saffron concentration in large-scale food production is 5-10 mg per kg.
- In sauce manufacturing, saffron performs best when infused in oils or emulsions, ensuring better dispersion in mass production.
3. Saffron as a Natural Food Coloring & Flavor Enhancer
- Unlike synthetic dyes, saffron’s crocin content (3-5%) makes it a safe, natural alternative for enhancing product appearance.
- Studies show that saffron-based coloring remains stable up to pH 5.5, making it ideal for dairy, bakery, and beverage applications.
For companies integrating saffron into industrial food production, scientific formulation and processing techniques are crucial for maintaining its quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Maximizing Saffron’s Shelf Life & Potency
Proper storage and preservation techniques can extend saffron’s potency, color vibrancy, and aroma stability. Scientific studies highlight the impact of temperature, humidity, and packaging on saffron’s degradation rate.
1. Best Storage Conditions for Preventing Degradation
- According to research in the Journal of Food Preservation (2022), saffron should be stored at 15-20°C, with humidity levels below 40% to maintain its bioactive compounds.
- Exposure to light and oxygen reduces crocin levels by up to 30% in three months, making vacuum-sealed glass containers the best storage solution.
2. Prevention of Oxidation & Flavor Loss
- Freeze-drying saffron retains 95% of its volatile aroma compounds compared to traditional drying methods.
- Nitrogen flushing in commercial packaging reduces oxidation by 60%, extending saffron’s usability in bulk production.
3. Freeze-Drying & Microencapsulation for Extended Shelf Stability
- Microencapsulated saffron powder maintains its aroma and potency for up to 24 months in commercial food production.
- Freeze-dried saffron extracts preserve over 90% of their bioactive compounds, making them suitable for pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals.
By adopting advanced preservation methods, businesses can minimize waste, maintain consistent product quality, and improve saffron’s shelf stability in large-scale production.
Saffron Pairing Guide: Best Ingredients to Use for Maximum Flavor
Saffron’s complex flavor profile allows for strategic ingredient pairing, enhancing sweet, savory, and aromatic food and beverage applications.
1. Saffron & Dairy: Enhancing Creamy Textures
- Saffron’s fat-soluble compounds bind well with dairy, amplifying its aroma and depth.
- In desserts like saffron-infused panna cotta, studies show crocin’s stability increases by 20% when combined with milk proteins.
2. Saffron & Citrus: Balancing Bitterness & Sweetness
- Saffron pairs well with lemon, orange, and yuzu, balancing its bitter and earthy notes.
- A study in Food Chemistry (2023) found that saffron enhances citrus-based flavor retention by 30%, making it ideal for premium beverages.
3. Saffron & Herbs & Spices: Best Combinations
- Cardamom, cinnamon, and vanilla intensify saffron’s warm, floral notes.
- In Persian and Indian cuisines, cumin and saffron are used together to enhance umami flavors in rice dishes.
Strategic saffron pairings can improve flavor complexity and consumer appeal in gourmet and industrial food production.
Saffron as a Premium Ingredient for Brand Differentiation
Saffron’s luxury status makes it a key differentiator in the global food and beverage market. Premium brands leverage saffron to justify higher pricing and attract health-conscious consumers.
1. The Future of Saffron in Culinary & Beverage Trends
- Global saffron consumption is expected to grow by 7.3% annually, with increased demand in luxury teas, gourmet foods, and plant-based nutrition (Source: Fortune Business Insights, 2023).
- Functional saffron-based beverages targeting stress reduction and cognitive health are projected to dominate the RTD market.
2. How Companies Leverage Saffron for Premium Product Positioning
- Luxury chocolate brands use saffron for its exclusive appeal and natural golden hue.
- Plant-based meat companies integrate saffron to enhance color and antioxidant content, differentiating their products from competitors.
3. Final Takeaways: How to Get the Best ROI from Saffron Usage in Your Business
- Optimize saffron concentration for cost-effective formulations.
- Use advanced infusion techniques to retain bioactive compounds and aroma.
- Leverage saffron’s premium status in marketing to enhance brand positioning and consumer perception.
By integrating saffron into premium, functional, and innovative food and beverage products, companies can achieve higher market differentiation and profitability.
Saffron: A Strategic Ingredient for Culinary & Beverage Innovation
Saffron is not just a spice; it is a powerful asset in the food and beverage industry. Companies that master saffron infusion techniques gain a competitive edge by offering superior taste, aroma, and color in their products. With the global saffron market projected to reach $1.6 billion by 2028 (Source: Fortune Business Insights), optimizing saffron applications is more critical than ever.
Scientific research highlights that crocin and safranal degrade by up to 30% when exposed to direct heat over 70°C, making cold infusion and controlled extraction essential for preserving quality. Studies by Food Chemistry Journal (2021) confirm that saffron’s antioxidants are maximized when infused in fat-based mediums, making dairy and oil-based applications ideal.
For businesses in the culinary and beverage sector, strategic saffron utilization can improve product appeal, enhance branding, and even justify premium pricing. Whether you’re developing gourmet meals, signature drinks, or functional beverages, applying scientifically-backed saffron techniques will elevate your products. Invest in saffron the right way, and let its golden magic transform your creations!